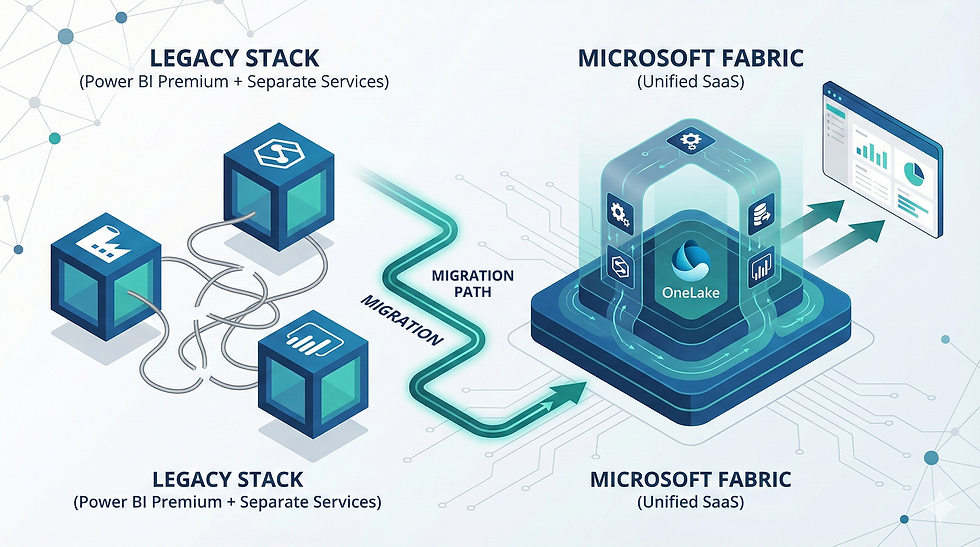
Your Business Data Analyst Checklist: What to Expect From Professional Services
- Matt Lazarus

- Jun 9, 2025
- 6 min read
Updated: Sep 16, 2025
Every business leader knows that feeling. Mountains of data accumulate daily—sales figures, customer interactions, operational metrics—yet extracting meaningful insights remains frustratingly elusive. The information exists, but transforming it into strategic decisions proves challenging without proper expertise.
This scenario highlights a critical gap in modern business operations. Organizations possess valuable data assets but lack the specialized skills to leverage them effectively. Professional data analysis services bridge this gap, turning raw information into competitive advantages.
The Hidden Components of Professional Data Analysis That Most Businesses Miss
A common misconception limits the perceived value of professional business data analyst services. Many executives assume these specialists simply create attractive visualizations or generate standard reports. This narrow view overlooks the comprehensive strategic value that experienced analysts bring to organizations.
Discovery Phase: Uncovering Hidden Data Assets
Professional data analysis begins with systematic discovery. Analysts conduct thorough investigations of existing data ecosystems, revealing forgotten or underutilized information sources. Legacy systems frequently contain historical information providing crucial context. Departmental databases house specialized data never integrated into central reporting.
Customer service platforms capture behavioral insights overlooked by standard analytics.
The discovery process extends beyond simple inventory. Analysts assess data quality, identify integration opportunities, and map information flows across departments. This systematic approach ensures no valuable data remains hidden or underutilized.
Infrastructure Assessment: Diagnosing System Health
A thorough infrastructure evaluation forms the foundation of effective data analysis in business. Professional analysts examine technical architecture with diagnostic precision. They identify why reports generate slowly, pinpoint data inconsistencies between departments, and discover bottlenecks limiting analytical capabilities.
Infrastructure assessment covers database performance, data integration quality, and reporting system efficiency. Analysts evaluate whether current systems support advanced analytics or require upgrades. This comprehensive review provides a roadmap for technical improvements alongside analytical insights.
Stakeholder Alignment: Creating Unified Vision
Different departments naturally develop distinct metrics. Sales teams focus on pipeline conversion, marketing tracks engagement rates, and operations monitor efficiency ratios. Professional data analyst responsibilities include harmonizing these varied perspectives into cohesive analytical frameworks.
Experienced analysts facilitate structured discussions with stakeholders. They document specific needs, identify shared objectives, and resolve conflicting priorities. This process creates consensus around data definitions, reporting requirements, and strategic goals.
Customized Methodology Development
Generic analytical approaches rarely address specific business challenges effectively. Professional services develop tailored methodologies reflecting industry dynamics, competitive pressures, and organizational capabilities. Manufacturing companies require different frameworks than professional services firms.
Customization extends beyond industry considerations. Company size, growth stage, and strategic objectives influence analytical design. Professionals create frameworks that evolve with organizations, providing flexibility while maintaining analytical rigor.

The Transformation Process: From Raw Data to Strategic Intelligence
Understanding how professionals transform disorganized data into strategic assets helps organizations maximize their analytical investments. The process combines technical expertise with business acumen, creating insights that drive meaningful improvements.
Data Validation and Quality Assurance
Before meaningful analysis begins, data requires careful validation. Professional analysts employ systematic protocols ensuring accuracy and consistency. They cross-reference information across sources, investigate anomalies, and reconcile conflicting records.
Quality assurance extends beyond error correction. Analysts standardize formats, establish naming conventions, and create data dictionaries. They document assumptions, note limitations, and establish confidence levels for different data sources. This foundation ensures analytical conclusions rest on solid ground.
Advanced Analytical Applications
Professional data analysis in business extends far beyond basic reporting. Experienced analysts apply sophisticated techniques, revealing insights invisible to standard approaches.
Predictive modeling anticipates future trends based on historical patterns and external factors. These models help organizations prepare for market changes, adjust inventory levels, and optimize resource allocation.
Correlation analysis identifies relationships between seemingly unrelated variables. Professional analysts might discover that employee satisfaction scores predict customer retention rates or that weather patterns influence product preferences.
Advanced segmentation divides customers, products, or processes into meaningful groups. Unlike simple demographic sorting, professional segmentation uses behavioral patterns, purchase histories, and predictive indicators.
Pattern Recognition and Strategic Synthesis
Professional analysts combine statistical expertise with business understanding to identify meaningful patterns. They recognize seasonal variations masked by growth trends, detect early warning signals for customer churn, and spot emerging opportunities before competitors.
The synthesis process transforms individual findings into comprehensive strategic recommendations. Analysts consider organizational capabilities, competitive dynamics, and implementation feasibility. They prioritize opportunities based on potential impact and required resources.
Implementation Planning
Raw insights require translation into executable strategies. Professional services develop detailed implementation plans including:
Specific actions and responsible parties
Realistic timelines and milestones
Required resources and budget estimates
Success metrics and monitoring protocols
Risk mitigation strategies
This comprehensive planning reduces implementation failures and ensures realistic expectations for data-driven decision making.
Deliverables, Communication, and Ongoing Partnership Excellence
Professional data analysis services deliver comprehensive outputs designed for different organizational needs. Understanding these deliverables helps organizations maximize value from analytical engagements.
Comprehensive Reporting Architecture
Executive leadership receives concise strategic summaries highlighting critical findings and recommended actions. These documents focus on business impact, enabling quick decision-making. Implementation teams get detailed analytical reports including methodology explanations, assumption documentation, and technical specifications.
Technical teams receive implementation guides with specific requirements and integration specifications. Visual dashboards provide ongoing monitoring capabilities, replacing static reports with dynamic insights. Professional services ensure these tools align with existing infrastructure while introducing advanced capabilities.
Strategic Communication Frameworks
Communication strategies adapt to stakeholder preferences and project phases. Some executives prefer weekly briefings during critical implementations, while others need monthly strategic reviews. Department heads might require tactical updates focused on their operational areas.
Professional partnerships recognize that data-driven decision making requires ongoing refinement. Markets evolve, customer preferences shift, and new data sources emerge. Effective services include mechanisms for continuous improvement, monitoring recommendation performance, and adjusting strategies based on results.
Sustainable Knowledge Transfer
Knowledge transfer ensures sustainable analytical capabilities. Professional services provide hands-on training using actual company data, create comprehensive documentation, and establish decision frameworks. They build internal confidence through mentoring and gradual responsibility transfer.
Success measurement begins with clear metrics established during initial engagement. Professional services track tangible outcomes, including revenue impact, cost reductions, and efficiency improvements. Regular reviews demonstrate value and identify areas for continued focus.

Maximizing Value from Professional Analysis
Organizations enhance returns from professional analytical services through proper preparation and engagement. Data accessibility accelerates analytical projects. While professionals work with imperfect data, basic organization, and documentation, speed initial phases.
Leadership commitment drives organizational adoption. When executives champion data-driven decision-making, cultural resistance diminishes. Internal champions facilitate knowledge transfer and adoption. Assigning dedicated team members to work alongside external analysts accelerates learning.
Realistic timelines prevent disappointment. While some insights emerge quickly, comprehensive transformation requires patience. Organizations should expect iterative improvements rather than instant revolution.
Strategic Next Steps
Professional business data analyst services provide more than technical expertise. They transform how organizations perceive and utilize information assets. From initial discovery through ongoing optimization, these services build competitive advantages through superior decision-making.
The investment returns value through revenue optimization, cost reduction, improved agility, and enhanced strategic planning. Organizations gain confidence in decisions backed by rigorous analysis rather than intuition alone.
Success requires choosing appropriate partners, demonstrating clear methodologies, relevant experience, and commitment to knowledge transfer. Organizations ready to advance their analytical capabilities should assess their current state honestly. What questions remain unanswered? Which decisions rely on guesswork? Professional data analysis services provide the expertise to unlock competitive advantages.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it typically take for a business data analyst to deliver initial insights after starting a project?
Initial findings typically emerge within two to four weeks of project initiation. Simple analyses with well-organized data may yield insights within days. Complex multi-system investigations require longer discovery phases. Most professional engagements provide preliminary observations within the first fortnight. Comprehensive strategic recommendations generally require six to eight weeks for thorough analysis and validation.
What's the difference between hiring a freelance business data analyst versus working with a professional analytics firm?
Freelance analysts offer specialized expertise for defined projects with clear boundaries. They provide flexibility and potentially lower costs. Professional firms bring institutional knowledge, established methodologies, and team redundancy. Firms offer peer review processes, specialized tools, and scalability. The choice depends on the project's scope, complexity, and long-term analytical needs.
How do I know if my current data infrastructure is ready for professional business data analyst services?
Organizations with accessible primary data sources can begin professional engagements immediately. Warning signs indicating preliminary work include data existing solely in email attachments, the absence of historical records, or conflicting data versions across departments. Most professional services include infrastructure assessment within their scope. Professional analysts work with imperfect data but cannot analyze inaccessible information.